Our latest research article on the optical properties of self-assembled quantum dot crystals has just been published as an Accepted Manuscript in the Journal of Materials Chemistry C.
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/tc/c8tc04780d#!divAbstract
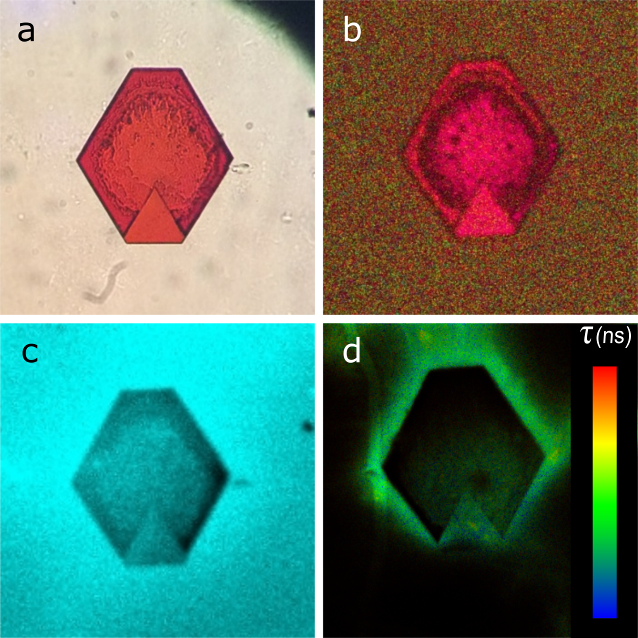
This research was undertaken as part of our collaborative work with ITMO University, St Petersburg, Russia. In this paper, quantum dot (QD) self-assembly into ordered superstructures has been analysed, along with the evolution of their morphological and optical properties. QD self-assembly occurs through two distinct stages (homo- and hetero-geneous), leading to the formation of supercrystals with a layered morphology. Analysis of the optical properties throughout the superstructures’ growth has shown that the absorption and photoluminescence (PL) bands are blue shifted, retaining almost the same PL lifetimes as in the initial QD solution. The supercrystals formed possess a further unique optical property caused by their layered morphology; namely, a four-fold symmetry characterized by strong birefringence. Such supercrystals may be used for the fabrication of microscale optical paths with high extinction coefficients and specific polarization properties for novel optoelectronic devices.